Healable 2D Sulfur Iodide: The Next Big Thing in Lithium-Sulfur Battery Technology
Healable 2D Sulfur Iodide: The Next Big Thing in Lithium-Sulfur Battery Technology
Advantages of all solid- state lithium-sulfur batteries with sulfur- iodide cathode
The pursuit of rechargeable batteries characterized by high energy density, enhanced safety, extended cycle life, and affordability remains a critical objective for various electrochemical storage applications, including portable electronics and electric vehicles. Among the diverse range of alternative battery technologies, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are recognized as a promising next-generation energy solution, primarily due to their high theoretical energy density, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. Nevertheless, current lithium-sulfur batteries, which typically employ sublimed sulfur-based cathodes and ether electrolytes, encounter several significant challenges. Key issues include the insulating properties of sulfur and its sulfides, the shuttling effect caused by soluble lithium polysulfides (LiPS), and the growth of dendrites on the metallic lithium anode, all of which hinder the development of stable and high C-rate Li-S batteries. Sulfur-iodide cathode introduces an innovative approach to addressing several key challenges associated with the commercialization of Li-S batteries. Sulfur-iodide effectively disrupts the intermolecular bonds that hold sulfur molecules together, adjusting the melting point to an optimal range. The reduced melting point of novel cathode material facilitates the repair of interfaces, which has been a long-desired solution for these batteries.
Image Credits: Author photo: Dr Kiai
Utilizations and prospective developments
Sulfur-iodide cathodes present a promising option due to their highly reversible redox reactions, rapid electrochemical kinetics, and significant redox potential. Additionally, Sulfur-iodide demonstrates considerable chemical stability in most commonly used solvents, including water. These benefits create new possibilities for various electrolyte-electrode configurations tailored for practical applications that require both high energy density and enhanced safety. The integration of sulfur and iodide improves the overall conductivity of the material while reducing its melting point. Regular remelting of the sulfur iodide material can restore interfaces that have been compromised due to cycling. A solvothermal reaction could be used to make 2D sulfur iodide nanosheets, which would effectively combine sulfur and iodide into a nanocomposite. This innovative design significantly improves the structural stability and electrical conductivity of sulfur iodide cathodes. By facilitating the concurrent formation of carbon encapsulation layers and crystalline sulfur iodide cores, the resulting nanocomposite cathode materials will show remarkable compactness, conductivity, and structural integrity. The thermodynamic instability of sulfur iodide can be significantly mitigated through the chemical absorption or physical immobilization of molecular iodide on carbon matrices with high specific surface area. The porous nature of carbon, combined with its electronic conductivity, facilitates rapid charge transport pathways, thereby enhancing the rate capability. The implementation of iodide/carbon cloth cathodes could open up new possibilities for this category of cathodes in the development of flexible and wearable devices.
The Future of Solid-State Batteries
In the future, two-dimensional nanomaterials composed of sulfur iodide are expected to possess significant application potential across various domains, including nanotechnology, electronics, optoelectronics, and energy storage, due to their distinctive structures and characteristics. This finding may address one of the most significant obstacles to the implementation of solid-state Li-S batteries by substantially enhancing their longevity. The capacity for a battery to self-repair merely through an increase in temperature could greatly prolong the overall life cycle of the battery, thereby paving the way for practical applications of solid-state batteries.
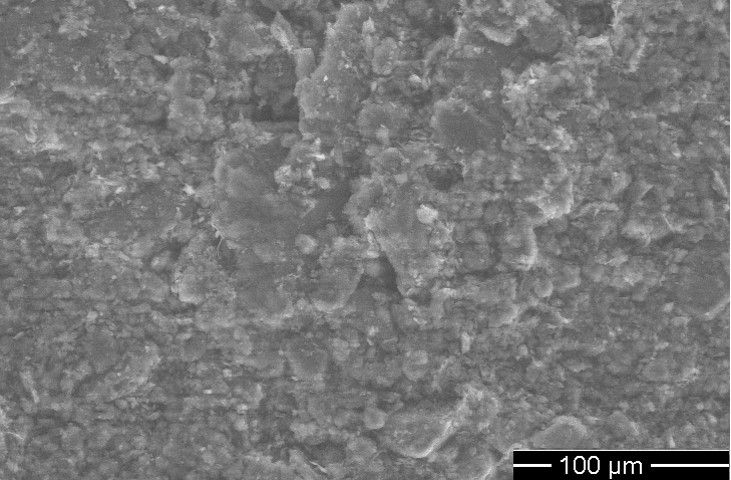
SEM image of sulfur-iodide carbon cathode
Image credits author Dr Kiai & Istanbul Technical university
References and Further Reading
Ma, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, Z., Cui, C., He, M., Huo, H., Yin, G. and Zuo, P., 2021. Iodine-doped sulfurized polyacrylonitrile with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium sulfur batteries in carbonate electrolyte. Chemical Engineering Journal, 418, p.129410.
Qian, M., Wu, F., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Song, T. and Tan, G., 2024. Healable and Conductive Two-Dimensional Sulfur Iodide for High-Rate Sodium Batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Zhou, J., Holekevi Chandrappa, M.L., Tan, S., Wang, S., Wu, C., Nguyen, H., Wang, C., Liu, H., Yu, S., Miller, Q.R. and Hyun, G., 2024. Healable and conductive sulfur iodide for solid-state Li–S batteries. Nature, 627(8003), pp.301-305.