National Green Hydrogen Mission of India
National Green Hydrogen Mission of India
The National Green Hydrogen Mission is an ambitious plan to achieve net zero emissions target by 2070 and towards the energy independence of India by 2047. This ambitious project not only focusses on reducing dependence on fossil fuels but also makes India a global leader in the development and production of electrolysers and other green hydrogen-enabling technologies. India plans to develop renewable resources of energy and become a leading producer and exporter of green hydrogen as well as byproducts like methanol and ammonia to set itself as a model for others.
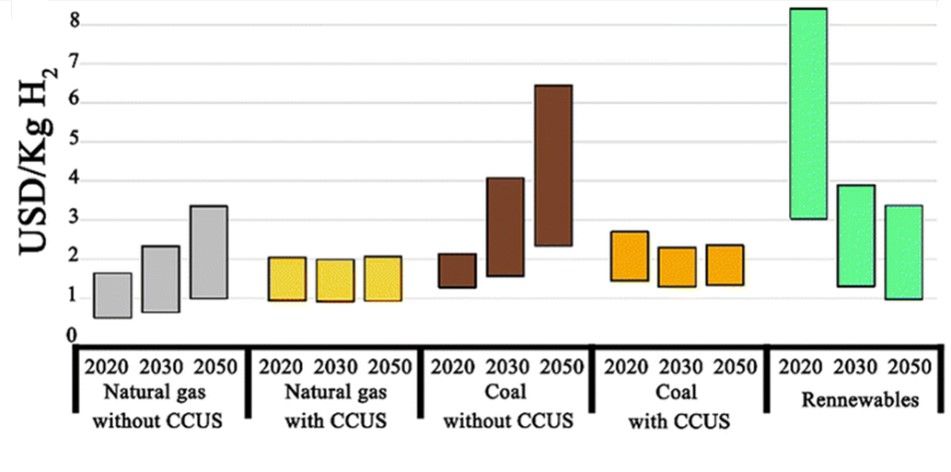
The mission will involve the development of at least 5 million metric tonnes (MMT) of green hydrogen annually by 2030. This will increase rapidly through export markets and global demand to up to 10 MMT. This is part of an urgent transition in exchange for hydrogen production from fossil fuels, as green hydrogen is produced from synthetic fuels like green ammonia and green methanol, which contribute greatly to the decarbonization of many industries.
The mission would be spending about ₹19,744 crores on different strategic elements to accomplish the objectives. The SIGHT Programme forms the basis of the objective with a budget of ₹17,490 crores. All the other components, like expenditure in pilots, research, and development, and all the other mission components, will help the mission accomplish its goal.
The strategy involves phased implementation for the National Green Hydrogen Mission. It will be divided into two phases: the first from 2022 up to 2025. It is going to focus on increasing demand as well as supply enablers of green hydrogen. This involves trying to ramp up electrolyser manufacturing capacity and pilot projects, along with efforts toward creating a legislative framework to encourage industry growth. From 2026 to 2030, the second phase increases production when green hydrogen starts to become competitive with fossil fuels, while research and development continue to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
This National Green Hydrogen Mission is poised to generate very important economic as well as environmental benefits. The mission is likely to attract investments of over ₹8 lakh crore by 2030-end, which would work wonders for the economy. It would also likely create over 6 lakh full-time jobs and, therefore, support growth and stability in the economy. The environmental objective of the mission is to avoid about 50 million metric tons of CO2 emissions every year, completely in line with the aim of India promoting sustainable development. Summing it up, the National Green Hydrogen Mission is an important step in the right direction toward accomplishing India's energy and climate goals. With a planned strategy for deployment, strong support in its regulations, and high emphasis on cutting-edge technologies, India can really become a worldwide leader in the green hydrogen space. It reflects India's commitment to sustainable energy utilization of its abundant renewable resources with its mission to enhance energy security-becoming a source of inspiration for the rest of the world towards shifting to a more sustainable future.
Image source & Credits: AI has been used to generate the image only for visualization purpose
References & Further Reading
- https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-pro...
- Lepage, T., Kammoun, M., Schmetz, Q. and Richel, A., 2021. Biomass-to-hydrogen: A review of main routes production, processes evaluation and techno-economical assessment. Biomass and Bioenergy, 144, p.105920.
- Obiora, N.K., Ujah, C.O., Asadu, C.O., Kolawole, F.O. and Ekwueme, B.N., 2024. Production of hydrogen energy from biomass: Prospects and challenges. Green Technologies and Sustainability, p.100100.