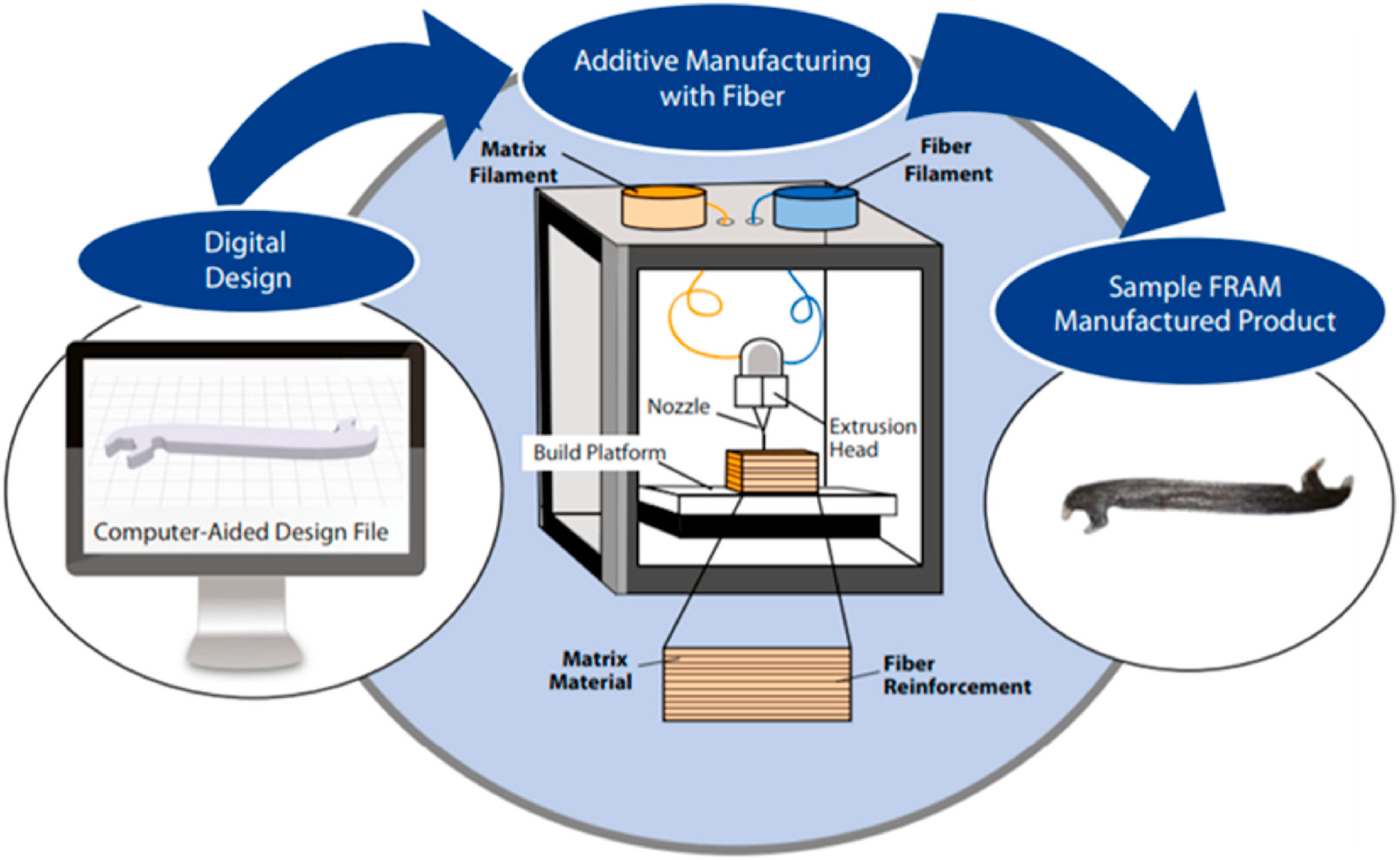
Turning Air into Drinking Water: Can This Technology Quench People's Thirst?
Turning Air into Drinking Water: Can This Technology Quench People's Thirst?
Image is for visualization purpose only GEMINI
A World Running Dry
Access to clean, fresh water is a fundamental human right, yet it's a right denied to millions across the globe. The statistics paint a grim picture: nearly 770 million people that's one in ten people on the planet lack access to safe drinking water. In many regions, the burden of water collection falls disproportionately on women and girls, who often spend hours each day trekking long distances to haul heavy containers of water.
India, with its burgeoning population and limited freshwater resources, faces a particularly acute water crisis. Major cities are teetering on the brink of "Day Zero," a terrifying scenario where taps run dry. Mismanagement and pollution have rendered many traditional water sources unusable, while groundwater is being depleted at an alarming rate. Climate change further exacerbates the situation, with deforestation and changing weather patterns contributing to water scarcity. The 2018 Composite Water Management Index (CWMI) report by NITI Aayog paints a stark picture: 600 million Indians face high to extreme water stress, and an estimated 200,000 people die each year due to inadequate access to safe water. By 2030, the country's water demand is projected to outstrip supply by twofold, threatening severe scarcity and potentially impacting India's GDP.
A Solution in the Air We Breathe?
As traditional water sources dwindle, the need for alternative solutions becomes increasingly urgent. One promising avenue is atmospheric water generation (AWG), a technology that literally pulls water from thin air. Even in the driest climates, the atmosphere contains a surprising amount of water vapor. AWG technologies capture this vapor and condense it into liquid water, offering a potentially revolutionary solution to water scarcity. The Earth's atmosphere holds an estimated 12,900 cubic kilometers of water, and this amount is predicted to increase in the coming decades. Even in Chile's Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth, fog and dew can generate a significant amount of water. This highlights the vast potential of AWG to tap into an abundant and renewable resource.
How Does AWG Work?
Several methods are used to extract water from the air:
- Desiccant materials: substances like silica gel absorb water vapor from the air. The material is then heated to release the vapor, which is condensed into liquid water.
- Active air cooling: Similar to how air conditioners work, this method cools the air below its dew point, causing water vapor to condense.
Innovations on the Horizon
Scientists and engineers are constantly pushing the boundaries of AWG technology. Promising new approaches include:
- Thermo-responsive hydrophilicity switching (TRHS): This technique uses special materials that change their affinity for water in response to temperature fluctuations. At low temperatures, the material absorbs water vapor, and at high temperatures, it releases the water in liquid form.
- Deliquescent salt reverse osmosis (DESARO): This method employs deliquescent salts, which readily absorb moisture from the air. The resulting salt solution is passed through a reverse osmosis membrane to separate the water from the salt.
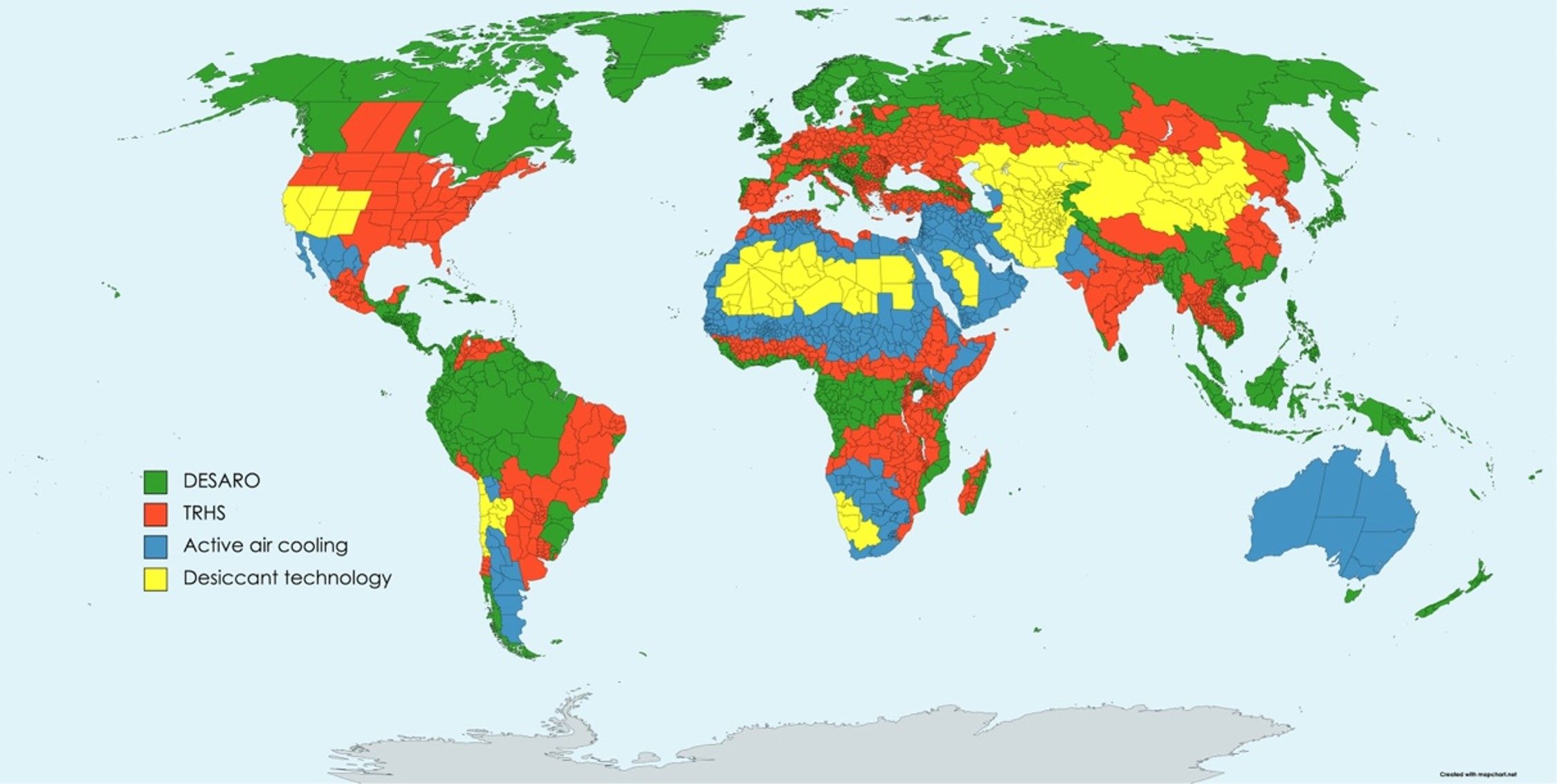
World map showing the preferred local water-from-air technology. Image reproduced with permission from (R. Peeters, et al., Fresh water production from atmospheric air: Technology and innovation outlook, iScience, 24, 103266, 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/...)
Companies
Pioneering AWG Technology
Across the globe, companies are
developing and deploying AWG solutions:
- Global Leaders:
- Watergen: An Israeli company specializing
in large-scale AWG systems, often used in disaster relief and to provide
drinking water in remote areas.
- Sky water Technology: A
US-based company offering a range of AWG solutions for residential,
commercial, and industrial use.
- Eole Water: A French company
focusing on wind-powered AWG systems, promoting sustainable water
solutions with minimal environmental impact.
- Watergen: An Israeli company specializing
in large-scale AWG systems, often used in disaster relief and to provide
drinking water in remote areas.
- Indian Innovators:
- Airowater: An Indian company
providing energy-efficient and affordable AWG purifiers for homes and
offices.
- Maithri Aquatech: A
startup developing solar-powered AWG systems to address water scarcity in
off-grid, rural communities.
- Uravu Labs: A startup
specializing in sustainable and energy-efficient AWG solutions, utilizing
renewable energy sources and innovative materials.
- Airowater: An Indian company
providing energy-efficient and affordable AWG purifiers for homes and
offices.
The Growing Market for AWG
The global air-to-water market is poised for significant growth, fueled by:
- Increasing demand: The
growing global need for clean drinking water and sustainable solutions is
driving demand for AWG technologies.
- Technological advancements: Continuous
improvements in AWG technology are leading to higher efficiency and lower
costs, making it more accessible.
- Government support: Supportive
policies and incentives are encouraging the adoption of AWG technology.
- Investments: Increased investment in research and development is accelerating the deployment of AWG solutions.
Despite its promise, AWG technology faces challenges:
- Energy consumption: Some
AWG systems, particularly those relying on refrigeration, can be
energy-intensive, leading to higher operating costs.
- Cost: The initial investment for AWG
systems can be substantial, making it less affordable for some individuals
and communities.
- Environmental impact: The
refrigerants used in some systems can have environmental implications if
not handled and disposed of properly.
- Water production: The amount of water produced by AWG systems is dependent on ambient humidity and temperature, which can be limiting in certain climates.
Ongoing research and development are focused on overcoming these challenges:
- Improving energy efficiency: Scientists
are exploring innovative cooling technologies and more efficient
refrigeration cycles to reduce energy consumption.
- Reducing costs: Advancements in manufacturing and
economies of scale are expected to drive down the cost of AWG systems.
- Minimizing environmental impact: Efforts
are underway to develop environmentally friendly refrigerants and alternative
cooling methods.
- Enhancing water production: Researchers are working to develop AWG systems that can operate efficiently in a wider range of humidity and temperature conditions.
Creative public-private partnerships are crucial to ensure wider distribution and accessibility of AWG technology, particularly in underserved communities. By collaborating, governments, businesses, and researchers can work together to make this life-saving technology available to those who need it most.
A Future Where Water Flows from the Sky
Air-to-water technology holds immense potential to address the global water crisis. By extracting water from the atmosphere, it offers a sustainable and innovative solution to water scarcity. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and increasing adoption are paving the way for a future where clean drinking water is accessible to all. By harnessing the power of innovation and embracing sustainable solutions like AWG technology, we can secure a water-rich future for generations to come.
References & Suggested Reading
- R. Peeters, et al., Fresh water production from atmospheric air: Technology and innovation outlook, iScience, 24, 103266, 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004221012359
- The Indian Startup Pulling Water From the Air Uravu’s new 1,000-liter-per-day unit will come on line this month. https://spectrum.ieee.org/water-harvesting
- Innovative air-to-water tech using liquid desiccant makes affordable, renewable water. https://india.mongabay.com/2024/08/innovative-air-to-water-tech-using-liquid-desiccant-makes-affordable-renewable-water/
- Turning air into water: The essential parts of air-to-water technology. https://a1rwater.com/featured/essential-parts-of-air-to-water-technology/
- Water to the people: a pathway through innovative technology and public-private partnerships. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/02/atmospheric...