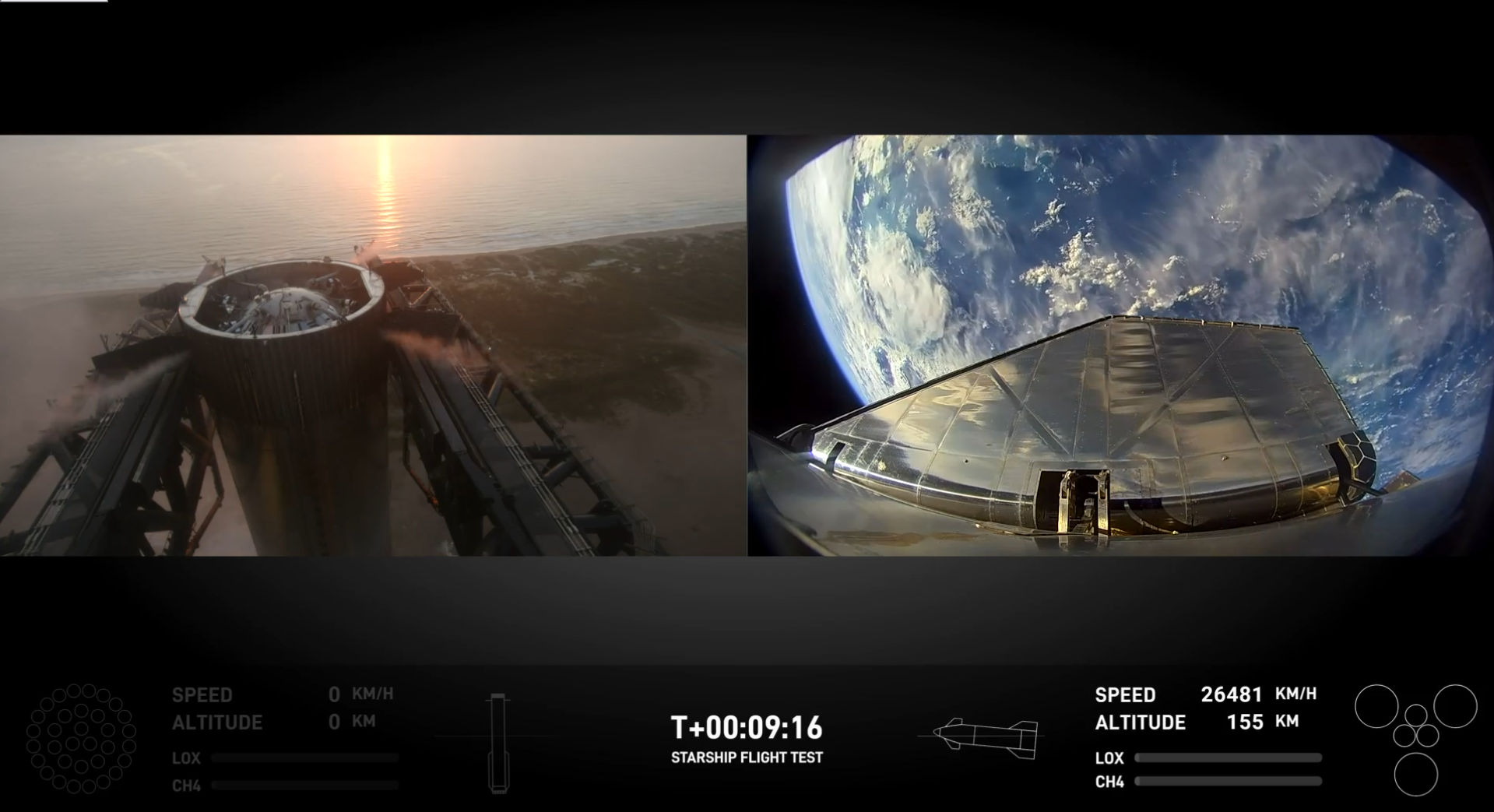
AI, Big Data & IoT in Geospatial Applications
AI, Big Data & IoT in Geospatial Applications
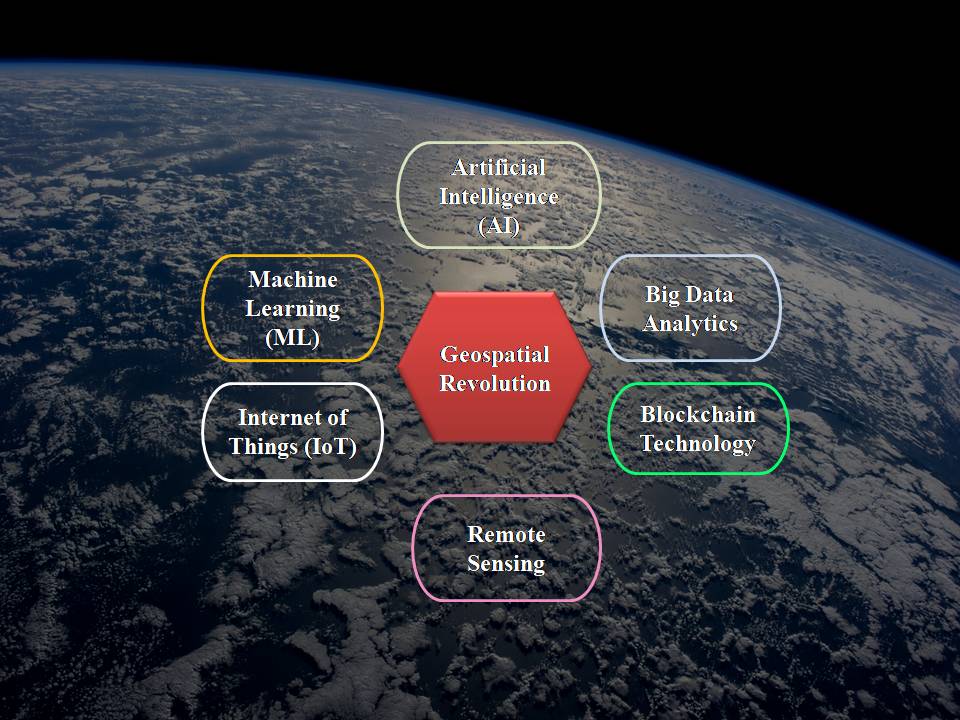
Re(G)eneration of Geospatial Technology in the E-Generation: The Role of AI, Big Data and IoT in Reshaping Geospatial Applications
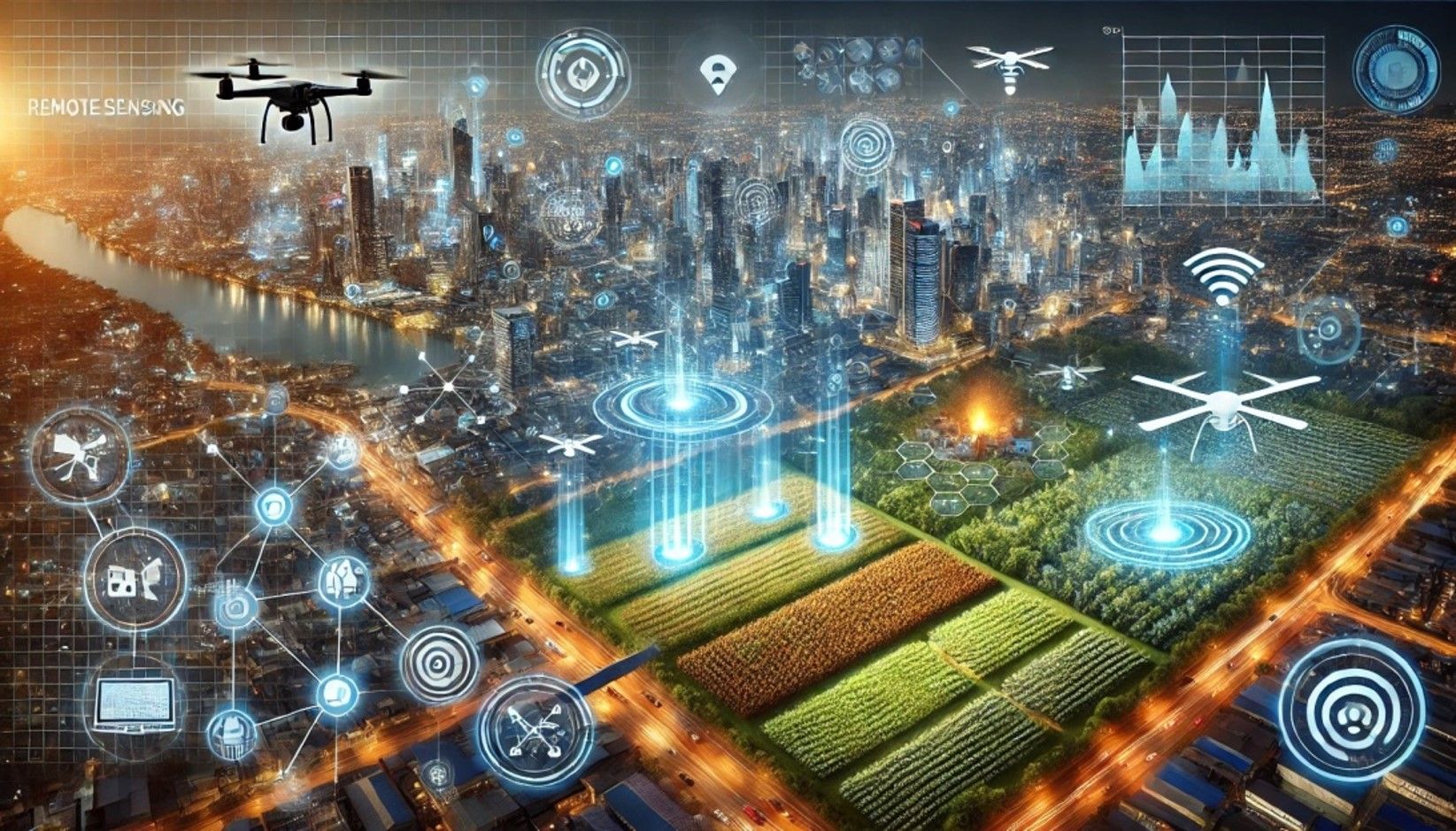
The evolution of advanced technologies like AI, Big data and IOT is transforming geospatial applications by transferring the traditional static datasets and analyzing methods to dynamic and smarter solutions. These technologies collectively unlock the potential for more efficient and proactive decision-making, driving more sustainable and resilient communities. This transformation is not only enhancing the scope of geospatial technologies but also enabling real-time insights that address complex global challenges. AI, for instance, is reforming the spatial data interpretation methods, including image recognition, pattern detection, and predictive modeling, which were once labor-intensive and cumbersome. Big data analytics, on the other hand, is driving the integration of vast and varied datasets from multiple sources, allowing the most holistic understanding of spatial patterns and trends. By processing large volumes of data in real time, it supports decision-making capabilities crucial for applications such as disaster management, environmental monitoring, urban planning, traffic management, public health surveillance, energy optimization, etc.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Geospatial Analysis: AI and ML are leading a new era in the geospatial field by automating data processing tasks and significantly boosting analytical capabilities. Algorithms, especially those based on deep learning, aid in processing large spatial datasets in real time with speed and precision. One of its key applications includes image classification and object detection, which utilize advanced techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNN), enabling AI to classify land cover, monitor ecosystem changes, and detect structures, including buildings and roads, from satellites or UAVs. Predictive analysis leverages historical geospatial data and is able to forecast future trends, from predicting urban growth and environmental transformations to tracking disease spread. The other applications include semantic segmentation (process that categorizes every pixel in an image based on feature type, such as water, forest or urban area), anomaly detection for infrastructure monitoring (algorithms which detect unusual patterns in geospatial data), automatic change detection (automatically tracking spatial and temporal changes over large areas), natural disaster and impact assessment, agriculture and crop monitoring, water resource management, etc.
Big Data: Enhancing Geospatial Data Processing: Rapid storage and analysis of big data, which encompasses massive volumes of structured and unstructured data from various remote sensing sources, makes real-time geospatial data accessible for critical applications like disaster response.
IOT and Real-Time Spatial Data Collection: By connecting physical devices via sensors, IOT facilitates real-time data transmission essential for dynamic geospatial analysis. In the context of smart cities, IOT sensors embedded in the infrastructure, such as traffic systems and buildings, help optimize city planning, transport, and energy management.
Blockchain for data security and transparency: Blockchain offers secure and transparent data storage, maintaining data integrated through a decentralized ledger. This is crucial for land title management and develops better supply chain and resource monitoring by enabling traceability of materials.
The "Re(G)eneration" of geospatial technology in the E-Generation is more than a technological shift; it’s a movement redefining how we interact with our world. By fusing AI, Big Data, and IoT into the fabric of geospatial science, we are unlocking insights and capabilities that were previously unimaginable. This transformation is reshaping everything from cities that anticipate our needs to ecosystems we can now protect in real-time. As we embrace this era, geospatial technology is no longer just a tool; it’s an evolving, intelligent partner guiding us toward a future of sustainable, connected, and informed living.
Image credits Author
References & Suggested Reading
1. X. X. Zhu et al., "Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources," in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 8-36, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307
2. Rafiq, I., Mahmood, A., Razzaq, S., Jafri, S.H.M., Aziz, I.: IoT applications and challenges in smart cities and services. J. Eng. 2023, 1–25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1049/tje2.12262